
Polyester staple fibre Industrial type

Specifications
| Trademark | Product Specification | Tensile strength, MPa | 180℃ dry heat shrinkage |
| CY510/511300 | 1.33/1.56dtex×38mm | 700 | 5.5 |
| Test method | GB/T 14337 | FZ/T 50004 |
Packing & Storage
| Packaging | The products leave the factory in the form of packaging bags or tanker shipments. The packaging bag should be a woven bag with a liner. It can be covered with polyethylene dust-proof film according to user needs. The tanker used to transport the product should be clean and dry. | |||
| Storage | The products are stacked in batches and should be placed in a cool, dry, ventilated warehouse with fire-fighting facilities, away from heat sources and avoiding direct sunlight. | |||
| Transportation | The product is non-dangerous goods. During transportation, loading and unloading, the product warning signs shall be implemented in accordance with the regulations, and preventive measures shall be taken to prevent the product from being damp, exposed to the sun, contaminated and damaged packaging, and shall not be thrown or unloaded. | |||
Free Quote
For samples, pricing, or more information, please call us at 0086 25 51192301 or mail to info@ascent-chem.com or fill out the following form.
We will respond to you as soon as possible.
Tel: 0086 25 51192301
E-mail: info@ascent-chem.com



General Information
Chemical & Physical Information
Safety Information
Synthetic Route
Chemical & Physical Information
| Common Names | Polyester staple fibre Industrial type | |||
| Structure | (C27H22O4S)n 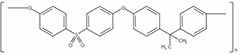 | |||
| CAS No. | 25135-51-7 | Melting point (℃) | 185 °C | |
| Molecular Weight | 1327.58 | Density | 1.24 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | |
| Appearance | White fibre | Refractive index | 1.633 | |
| HS Code | 39119000 | Autoignition Temperature | 550°C | |
| Solubility | Soluble in dichloromethane, dichloroethane, chloroform, chlorobenzene, benzene, toluene. | Glass transition temperature | 150 ℃ | |
Safety Information
| Safety Statement (Europe) | S24/25 | ||
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport | ||
| Water hazard class (WGK) | 3 | ||
| Personal protective equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. |
| Skin | Wash off with soap and plenty of water. |
| Eyes | Flush eyes with water as a precaution. |
| Inhalation | Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. |
Synthetic Route
| Polysulfone is polymerized from dialkali metal salts of diphenols (such as bisphenol A disodium salt) and active aromatic dihalides (such as 4,4`-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone). The production of polysulfone usually adopts Farnham’s nucleophilic substitution reaction. From the perspective of polymer synthesis, the production process of polysulfone products almost adopts the nucleophilic substitution polycondensation route in the industrial synthesis method. The production method has a one-step method and a two-step method. The two-step synthesis reaction is to generate bisphenol A disodium salt by in-situ reaction of bisphenol A and alkali, and then nucleophilic with 4,4`-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone Substitution reaction. The one-step synthesis of polysulfone is to use potassium bicarbonate or potassium carbonate instead of sodium hydroxide to synthesize polysulfone. This method can shorten the synthesis steps, avoid the dehydration process, and shorten the reaction time. It has great potential in increasing the output, but the current production Still use the two-step method to complete. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Text here, link
About Us
Ascent Petrochem Holdings Co., Limited is a company specializes in the processing and marketing industry chain of petrochem and coal chemical industry, by persistently pushing forward with high-tech and service innovation. We are committed to becoming China’s best diversified chemical company which focusing on technologies and services.
Contact Us
